
Bot Beats
Immerse yourself in an epic virtual robot multiplayer programming battle!

Immerse yourself in an epic virtual robot multiplayer programming battle!

Me and my brother's little game studio.
Technical Writing (Medium)
Technical Writing (Medium)
Technical Writing (Medium)
Play Store and AppStore
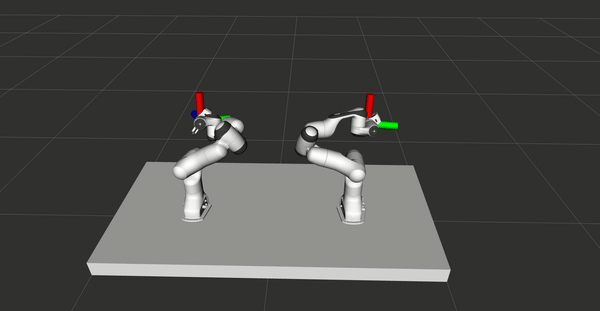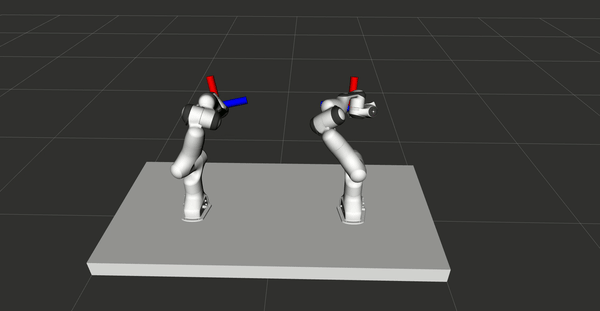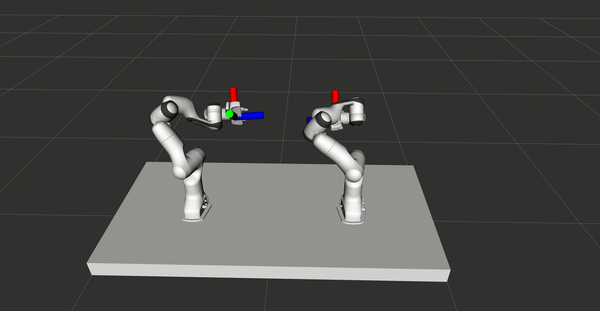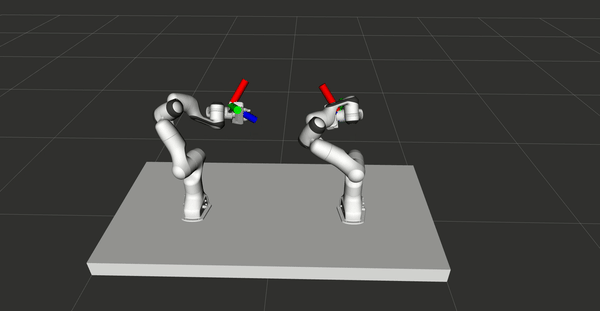
VR control for bimanual robots
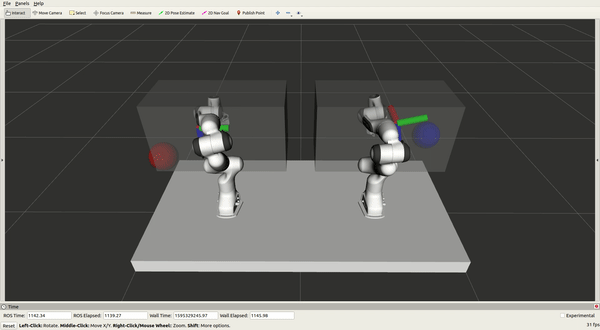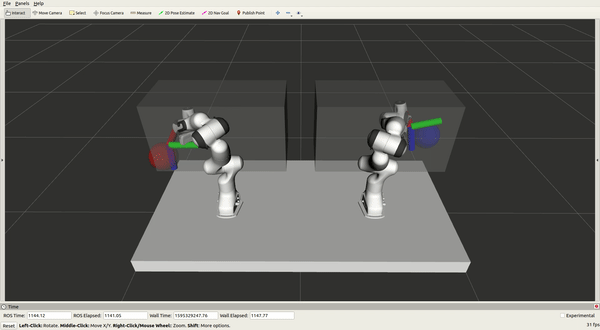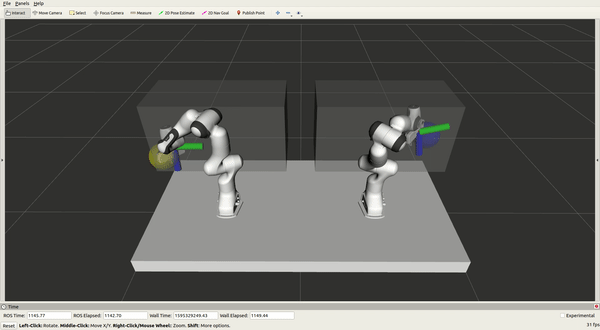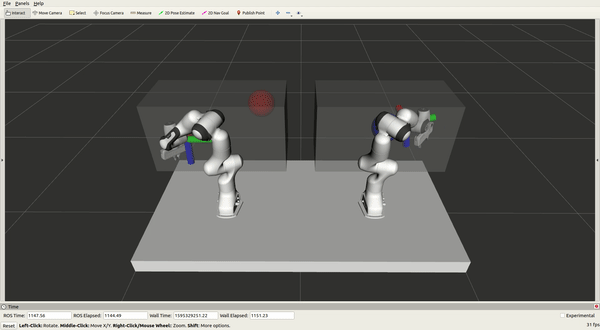
Experimenting on moveit_vive
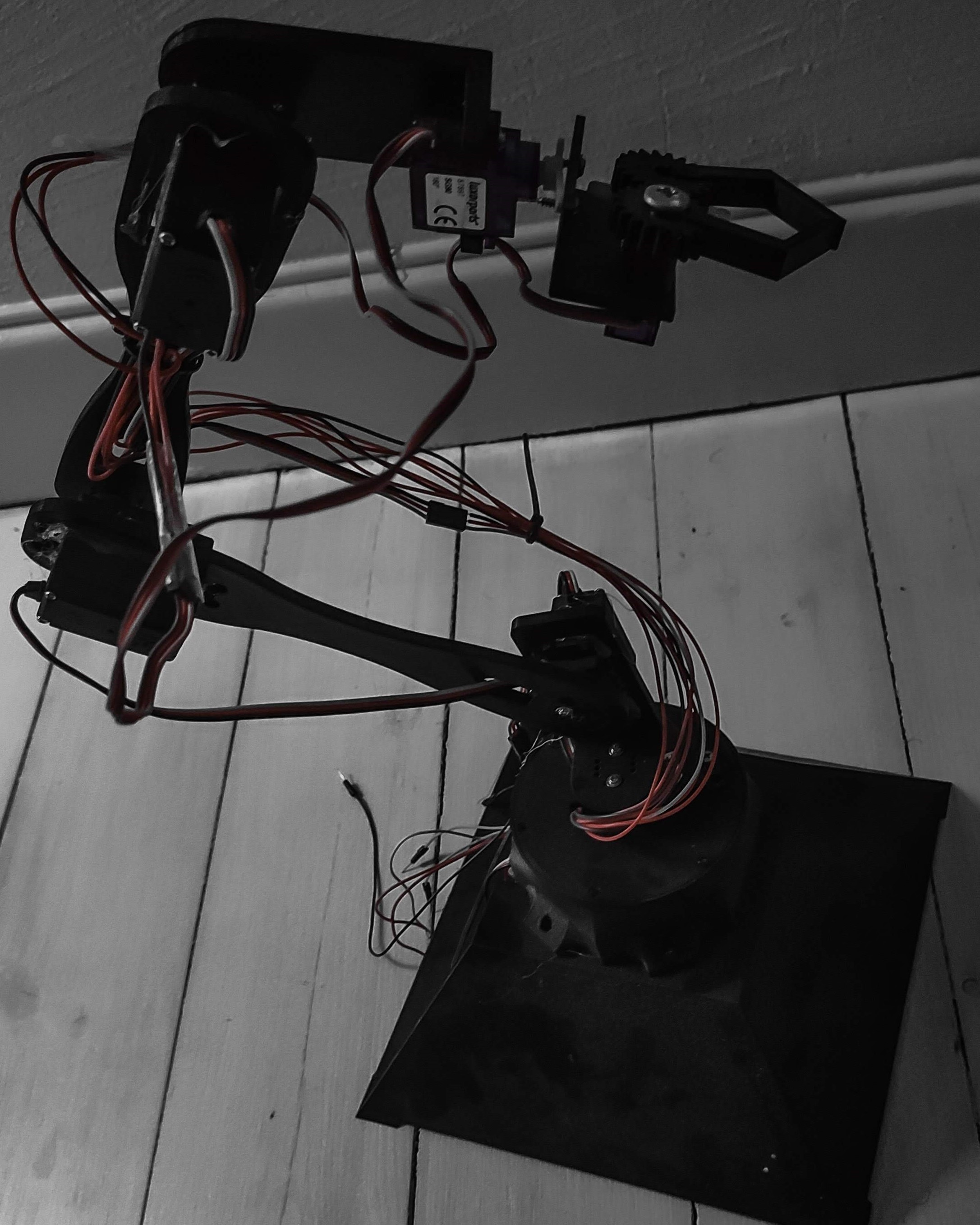

Custom built robotics arm using 3D printing, Raspberry Pi, Arduino and ROS
Abstract
With computers being used for more applications where commands can be spoken it is
useful to find algorithms which can separate voices from each other so that software
can turn spoken words into commands. In this paper our goal is to describe how
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) can be used for separation of voices in cases
where we have at least the same number of microphones, at different distances from
the speakers, as speakers whose voices we wish to separate, the so called "cocktail
party problem". This is done by implementing an ICA algorithm on voice recordings
containing multiple persons and examining the results. The use of both ICA
algorithms result in a clear separation of voices, the advantage of fastICA is that
the computations take a fraction of the time needed for the ML-ICA. Both algorithms
can also successfully separate voices when recordingsare made by more microphones
than speakers. The algorithms were also able to separate some of the voices when
there were fewer microphones than speakers which was surprising as the algorithms
have no theoretical guarantee for this.
Abstract
A control system used to control two Panda Franka Emika robots online and
simultaneously with two HTC Vive controllers is presented, with the primary purpose
of demonstrating tasks for robots. The system is validated by learning from
demonstration/imitation learning task via Principle Component Analysis (PCA). The
task consists of learning different bimanual movement patterns e.g. for drawing
sketches, with latent variables that then can be manipulated by the user to generate
new shapes of similar structure. Tasks of various correlations between the arms are
tested and compared. The system uses components and adaptations e.g. preexisting
modules for sensing, communication, motion planning, etc. to realize the goal of
modularity and support for other robots than the one used in this thesis. The most
prominent systems used are the Robot Operating System (ROS) for the base framework
for handling packages and sending information between different parts of the system,
and MoveIt’s planning library (running on ROS) for managing kinematics and
collision.